Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact. It is used in a wide variety of fields, but is particularly useful in Earth sciences such as hydrology, ecology, meteorology, oceanography, glaciology, and geology. It also has military, intelligence, commercial, economic, planning, and humanitarian applications.
Once the domain of satellite and aircraft data collection, remote sensing is now finding use cases much closer to home. The motion detectors protecting your home or business are a simple type of remote sensing and the self driving cars now under development rely heavily upon camera and LIDAR, two more type of remote sensing.
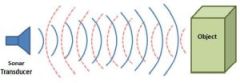
Passive sensors simply collect whatever signals reach the sensor. Active sensors, however, emit a signal and detect the reflection. For example, a common PIR (passive infrared) motion detector simply detects the heat of a human body and is therefore a passive sensor. The backup sensors common on the rear bumpers of cars emit an ultrasonic sound and sense the echo to detect an obstacle and are an example of active sensors.